Arthrosis (osteoarthrosis) is a disease of the joints that leads to their destruction.It affects 10% of the world's population.
When osteoarthritis is diagnosed, the symptoms are severe and the treatment of the disease must be comprehensive.
It is necessary to reduce stress, normalize nutrition, remove inflammation and alleviate muscle spasms.What are the characteristics of arthrosis, how to determine its occurrence and which treatment to choose?
Arthrosis - what is it?
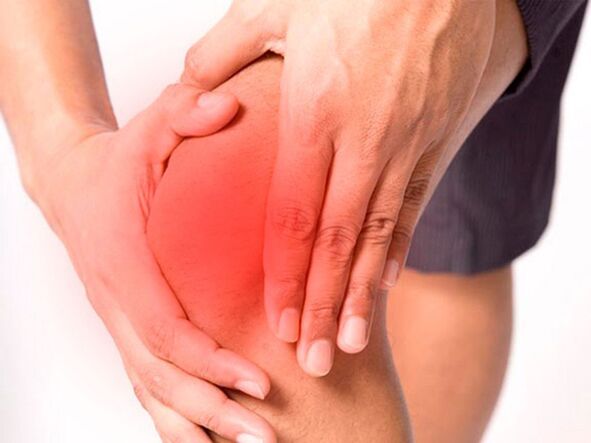
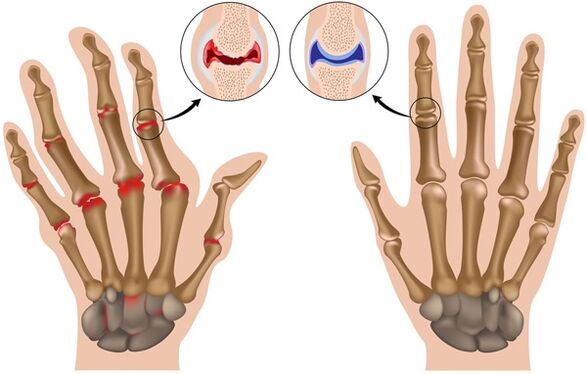
Arthrosis of the joints is degenerative changes in their structure, which are accompanied by pain and visible deformations.Another name of the disease, which is used in the international classification, is osteoarthritis.Let's look at the reasons why it occurs and how it is diagnosed.Osteoarthritis - what is it?
The disease begins with cartilage malnutrition and its destruction.The inner layer of cartilage becomes thin, the joint loses strength, and the bone tissue is filled with salts and growths (to restore strength).
That's why arthrosis is called deforming arthrosis - as it develops, the joint takes on an ugly "twisted" shape.
Deforming arthrosis has three stages of development:
- Osteoarthritis of the 1st degree - no noticeable symptoms, except for slight grinding and periodic pain when moving;
- Osteoarthritis of the 2nd degree - accompanied by the formation of growths, the appearance of noticeable pain, increased creaking, muscle weakness;
- Arthrosis of the 3rd degree is called an acute form of the disease.Acute arthrosis is accompanied by joint deformity and limited mobility.
Which joints are affected by osteoarthritis?
Deformations and inflammations most often affect the joints of the lower extremities - hips, knees, toes (most often the thumb).Less often – ankles and fingers.
However, it is possible for the disease to develop in other parts of the body.
In coxarthrosis, the hip joints are affected (untreated congenital dysplasia is often the cause of coxarthrosis).The destruction of the vertebral joints is called spondyloarthrosis, and the destruction of the knee joints is called gonarthrosis.Damage to several joints is called polyarthrosis.
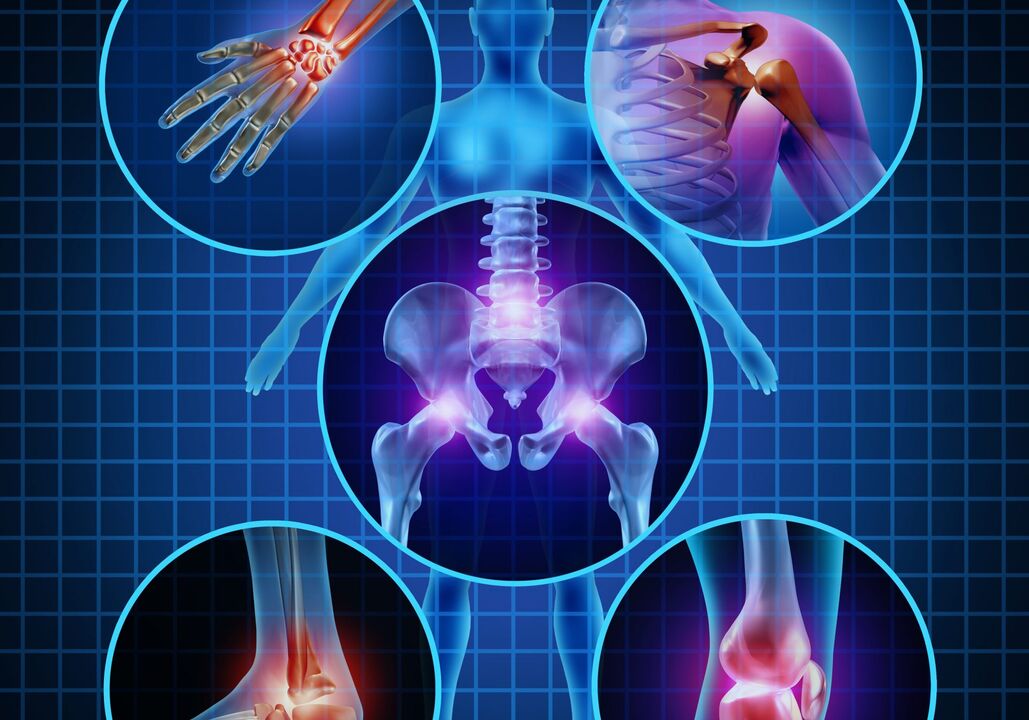
Symptoms of polyarthrosis are the severity of the general condition, spread of the process, curvature and pain in several joints at the same time (legs, arms, fingers, spine).
Inflammation in polyarthrosis spreads asymmetrically, affecting different bone joints in different ways.Once polyarthrosis is diagnosed, treatment varies in duration.
Causes of arthrosis
The occurrence of arthrosis is promoted by two reasons - stress and lack of adequate nutrition that supplies vitamins and minerals for tissue renewal.Every person's joints take stress.For athletes and dancers, during physical work the load on the legs is greater, which means that the bone joints wear out faster and require quality nutrition.With a quiet lifestyle, the supporting apparatus wears out more slowly, but also requires periodic tissue renewal.
Therefore, the main condition for the destruction and deformation of the joints is malnutrition and failure to absorb useful components, which often occurs due to metabolic disorders.
Here are the factors that contribute to joint wear and tear and metabolic disorders:
- Muscle weakness and improper joint loading.Weakness of one or more muscles increases the load on the joint and distributes it unevenly within the bony joint.Also, with flat feet and scoliosis, there is an irregular load on the muscles, so in these "harmless" diseases, the cartilage tissue wears out over the years and arthrosis appears.
The probability of arthrosis increases with intense physical activity.
If daily loads exceed the capabilities of bone tissue, they are formedmicrotraumas.In places of injury, thickenings appear, which grow over time and deform the joint;
- Metabolic disorders (gastrointestinal diseases - bile stagnation, dysbacteriosis, gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, metabolic diseases - diabetes);
- Psychosomatic causes - psychosomatics of arthrosis confirms that a negative emotional state also becomes a cause of the disease.Stress creates muscle spasms, constant stress disturbs the nutrition of all tissues (internal organs, bones, joints);
- Heredity (the type of metabolism and possible disorders is hereditary, the tendency to muscle weakness or improper formation of the bone apparatus, poor digestion - which is the basis for the development of arthrosis in old age).

Arthrosis is a disease of worn joints that have lost a significant supply of minerals and the ability to withstand stress and destruction.
Therefore, the susceptibility to the disease increases with age.After 70 years, arthrosis is diagnosed in every second pensioner.Since the maximum load falls on the legs (a person moves - walks, stands, runs, jumps), this is where the first signs of arthrosis appear.
Symptoms of arthrosis
Joint disease can be diagnosed by numerous painful symptoms - pain, swelling, creaking.
Symptom #1: Pain
The main symptom of the disease is joint pain.Its appearance is associated with the deformation of joint capsules and the formation of growths.
If you have osteoarthritis, pain symptoms will increase with movement and decrease with rest.
Or appear in an uncomfortable position and disappear when you choose a position that is comfortable for the leg and wrist.This is how arthrosis differs from arthritis, in which, on the contrary, it hurts more often at night, when resting, and hurts less during the day, when a person "walks".
At the beginning of the disease, pain appears periodically (with movement or uncomfortable position).As the disease progresses, the pain is felt more often and becomes stronger.It happens that rest does not bring relief, the joints hurt even at rest.Since blood circulation is already disturbed at that time, the joint becomes "sensitive" to weather changes ("turns", hurts).
Symptom no.2: screeching
Cracking occurs due to the loose mutual arrangement of the bones in the diseased joint in relation to each other.
However, mild crunching is also possible in healthy joint capsules (with weak ligaments, with hereditary mobile joints).
Arthritic creaking is characterized by growth.Over time, it intensifies, becoming louder and more expressive.
Symptom no.3: joint deformation and reduced mobility
This symptom appears as the disease progresses.It progresses along with increased pain and is associated with the growth of salt deposits, which prevent the joint from fully flexing and straightening.The deformity becomes noticeable in the later stages of the disease.First, the joint swells, then "bumps" appear, an unhealthy curve, "twisting" of the joint capsule is formed.
Treatment of joints with osteoarthritis
The treatment of arthrosis (osteoarthrosis) is based on two postulates - eliminating stress and ensuring adequate nutrition of the joints.How to treat osteoarthritis in order to achieve sustainable improvement and stop the destruction of cartilage and degeneration of bone tissue?The treatment of deforming arthrosis uses a complex approach.The patient is prescribed tablets and injections, bandages and physiotherapy.
When osteoarthritis is diagnosed, treatment cannot be unilateral.
You can't just feed the cartilage tissue with chondroprotectors or just relax the muscles.Unilateral measures will not help in dealing with such a serious disease.
How to properly treat arthrosis?During treatment, several areas of therapy are selected:
- Drug therapy: tablets, injections, blockades.In arthrosis, treatment with tablets, powders and capsules supplies the body with chondroprotectors.Preparations with chondroitin promote the synthesis of collagen, which nourishes and restores cartilage tissue.These are glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.They are produced in the form of arthrosis tablets, capsules or powder.They help in the initial stages of the disease and lose their effectiveness in advanced states, when the cartilage is almost completely worn out or destroyed.In that case, the patient undergoes surgery (endoprosthetics), replacing the destroyed joint with artificial tissue.Injections with anti-inflammatory and analgesic components - blockades - are also prescribed.And injections in the joint.In the case of arthrosis, with their help, gels that simulate intra-articular fluid, as well as painkillers and anti-inflammatory substances, are introduced into the bone joint.
Injections into the joint ensure that the medicine reaches the focus of inflammation.
The use of such injections allows you to reduce the number of tablets for arthrosis.Also, vitamin-mineral complexes are prescribed for tissue nutrition;
- Exercise therapy.For arthrosis, the doctor selects a set of gymnastic exercises to be performed independently at home.You can learn how to perform them in therapy practice classes at the clinic.

Gymnastics for arthrosis helps restore muscle tone and eliminate one of the causes of the disease - muscle fiber weakness;
- Physiotherapy treatment.This includes shock wave therapy (destroys large salt deposits, normalizes blood flow, activates own collagen synthesis), oxygen therapy (saturation of the joint with oxygen), massage (muscle relaxation and joint relief), electrotherapy, wave techniques;
- Diet food.When osteoarthritis is diagnosed, the course of the disease depends on diet.For osteoarthritis, the diet excludes all nightshade plants (potatoes, tomatoes, sweet peppers, eggplants).Also, nutrition for arthrosis limits alcohol, sugar, bakery products, confectionery products;
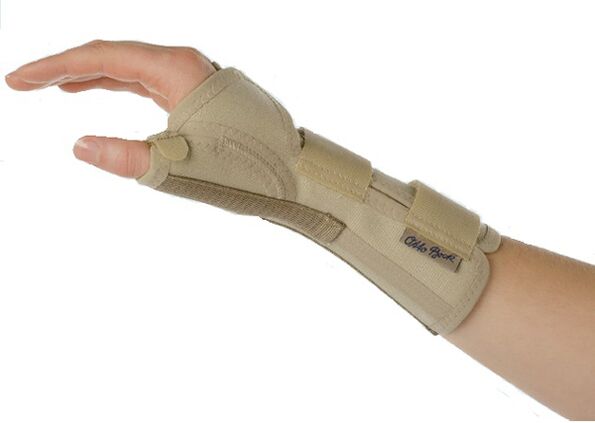
- Use of additional amplifiers(orthopedic corsets for joint support - orthoses);
- Alternative treatments.These include acupuncture (acupressure on reflex points that activate blood flow in certain parts of the body), homeopathic treatment and hirudotherapy.
For the successful treatment of arthrosis, it is necessary to apply the entire complex of the mentioned procedures and measures for several months (from 4 to 7).
Who treats arthrosis
Which doctor is a specialist in the treatment of arthrosis?We list the experts who can provide you with effective help:
- A rheumatologist is a doctor who treats with therapeutic methods (tablets, injections, physiotherapy);
- An arthrologist is a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of joint diseases, he knows the methods of conservative and surgical treatment, unfortunately a rare specialty;
- Orthopedist - usually works with patients on an outpatient basis, but in specialized research institutes, orthopedic surgeons perform surgical treatment;
- Therapist and surgeon are doctors available in every clinic;they are the ones you should contact to get a referral for the first examination and treatment.
Treatment of arthrosis with folk remedies
What can you do yourself?When osteoarthritis is diagnosed, treatment with folk remedies at home can often reduce pain and maintain mobility.
Osteoarthritis is often treated with gelatin (which the body uses to repair cartilage tissue).
Prevention of osteoarthritis
Prevention of deforming osteoarthritis consists of the following measures:
- Load limitation;
- Massage after physical activity;
- A complete healthy menu with vitamins, minerals, enzymes and bacteria (fermented dairy products), carbohydrates, fats and proteins;
- Controlling excess weight.
When osteoarthritis is diagnosed, the course of the disease depends on preventive measures, nutrition and the presence of physical (emotional) stress.
Disease prevention is recommended for those people whose work and daily activities involve increased stress on the joints.And for those whose age exceeds 45 years.
Osteoarthritis is easier to prevent than to treat.It is easier to maintain a joint in a healthy state than to restore cartilage tissue after its destruction.