Find out what arthrosis is and what types and degrees of this disease exist. Learn about the causes and symptoms of arthrosis, as well as methods of its treatment and prevention.
Arthrosis is a common disease of the musculoskeletal system associated with a disorder of the structure and function of the joints. The disease is chronic and usually develops gradually, and its manifestations intensify with age. Arthrosis can be determined by various signs, such as pain, limited movement, deformation of the joint, etc.
Arthrosis can occur in any joint, but large joints are most often affected: knee, hip, shoulder, elbow. The disease can also be classified into several types depending on which joint is affected. For example, there are maxillofacial arthrosis, digital arthrosis, spinal osteoarthritis and many others.
Each type of arthrosis has its own characteristics, but the common feature is the loss of joint function, which can lead to significant disruptions in the patient's life. In order to avoid serious consequences, it is important to contact a specialist at the first signs of the disease and start treatment in time, which can be medical or surgical.
Arthrosis: degrees and types of the disease
Degrees of arthrosis
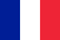
Arthrosis is a disease that develops gradually and goes through several stages. The degree of arthrosis depends on how badly the joints are affected and what changes have occurred in them. There are usually three degrees of arthrosis.
- First degree- in this stage of the disease, the patient may feel only minor joint pains after physical activity or prolonged stay in one position. It is also possible to lose noise when moving the joints.
- Second degree- in this stage of arthrosis, the pain becomes more intense, especially when moving, and swelling and movement of the bone in the joint is also possible.
- Third degree- the most serious stage of arthrosis, in which the pain syndrome becomes unbearable and the joint cannot fully perform its functions. In this case, urgent medical assistance is required.
Types of arthrosis
Osteoarthritis can affect different joints, but it most often occurs in the knees, hips, elbows and shoulders. The following types of arthrosis are distinguished.
- Knee arthrosis- This is one of the most common types of arthrosis affecting the knee joints. It can occur due to injury or overuse of the joints, as well as hereditary factors.
- Arthrosis of the hipis a lesion of the pelvic and hip joints, which often occurs in people over 50 years old or in those who have a predisposition to this disease.
- Elbow arthrosisis a disease that affects the elbow joint. It usually occurs due to injury or overuse of the joint, as well as repeated minor injuries that cause microtrauma to the joint.
- Osteoarthritis of the shoulderis a lesion of the shoulder joint that can occur either due to injury or due to various diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile arthritis.
In any case, it is necessary to monitor the condition of your joints and at the first signs of the disease consult a doctor in order to prevent the development of arthrosis.
Arthrosis: concept and causes of development
Arthrosis is a disease of the musculoskeletal system that leads to degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue of the joints. The disease manifests itself in the form of pain, stiffness of movements and deformation of the joint, which can lead to disruption of the patient's full life activity.
The main reason for the development of arthrosis is damage to the cartilage responsible for cushioning the joints. Damage can be caused by mechanical damage, increased load on certain areas, disturbed blood circulation and tissue nutrition.
The development of arthrosis can be influenced by various factors, such as age, heredity, metabolic disorders, obesity, hormonal disorders, as well as mechanical stress related to professional or household activities.
Types of arthrosis:
- Coxarthrosis (damage of the hip joint);
- Gonarthrosis (damage to the knee joint);
- Humeral arthrosis (damage to the shoulder joint);
- Radiocarpal arthrosis (damage to the carpal-radial joint);
- Interphalangeal arthrosis (damage to the interphalangeal joints of the fingers).
Radiography, computer tomography, magnetic resonance, as well as clinical and laboratory tests are used to diagnose arthrosis. Treatment includes conservative methods (medical therapy, physiotherapy, manual therapy), as well as surgical methods, including joint replacement.
Types of arthrosis
Arthrosis is a joint disease characterized by the gradual destruction of cartilage tissue. There are several types of arthrosis, each of which has its own characteristics and causes of development.
Osteoarthritis
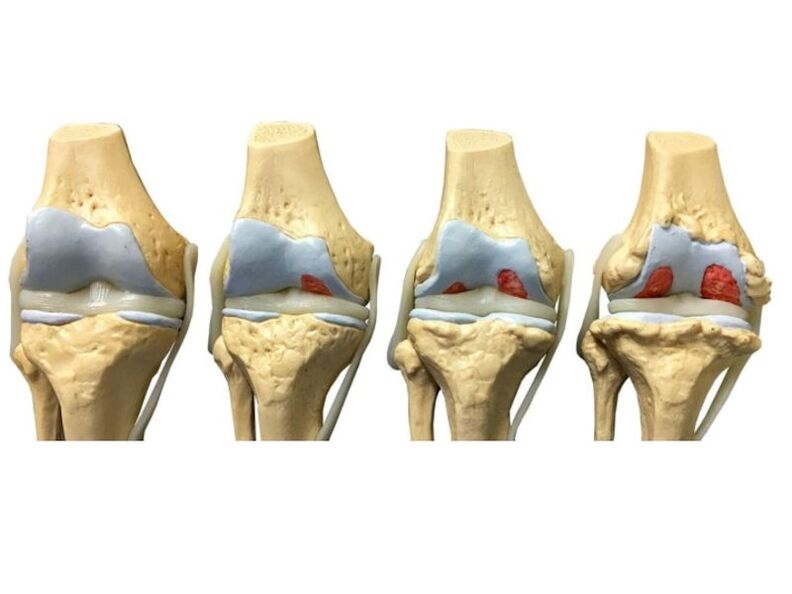
Osteoarthritis is the most common type of arthrosis, which occurs as a result of natural aging of the body and wear and tear of the joints. The peculiarity of osteoarthritis is the destruction of cartilage tissue, which leads to pain during movement and limited joint mobility.
Post-traumatic arthrosis
Post-traumatic osteoarthritis occurs as a result of an injury that damages the joint, such as a fracture. Reconstruction of the joint can lead to imperfect restoration of cartilage tissue, which can lead to the development of arthrosis.
Rheumatoid arthrosis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease associated with increased activity of the immune system. In this case, inflammation of the joints occurs, which leads to the destruction of the cartilage and deformation of the joints.
Summary:There are several types of arthrosis, each of which has its own characteristics and causes of development. Osteoarthritis is the most common type associated with natural aging and wear and tear of the joints. Post-traumatic arthrosis occurs as a result of joint injury, and rheumatoid arthrosis is associated with increased activity of the immune system and leads to joint deformation.
How does arthrosis occur?
Arthrosis is a chronic disease of the joints, which is characterized by the dysfunction of the cartilage, the structure and function of the bone and muscle substance. The development of arthrosis begins with the gradual wearing away of cartilage tissue, which leads to its dehydration, loss of elasticity and mobility. This causes degenerative changes in the joint, usually causing severe damage to the joint.
When the cartilage begins to wear out, its mechanical cushioning function is damaged and pathological contact develops between the joint segments. Worn bony limbs become rough and jagged, and protrude against the plane of the joint surface. This leads to disruption of the adhesion of joint surfaces to each other, increasing the load on them and the development of additional friction, which accelerates the wear of cartilage.
Thus, the development of arthrosis is associated with slow progression of cartilage damage, changes in bone tissue, reduction of synovial fluid and loss of its oily properties. Typically, the symptoms of osteoarthritis appear with age, but they can also occur as a result of joint injury or stress, as well as an unhealthy lifestyle, which reduces the tissue's ability to repair and maintain normal bodily functions.
Arthrosis: types, degrees, symptoms
What are the symptoms of arthrosis?
Arthrosis is a chronic disease of the joints that can lead to disruption of their functions and vital activity. This disease can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Joint pain. This is the most common symptom of arthrosis. Typically, the pain increases with movement and decreases with rest. It can be sharp or dull and painful.
- Limitation of movement in the joint. With arthrosis, you may feel that the joint has become stiff and cannot be moved. The patient may have difficulty bending or straightening the knee or elbow, for example.
- Creaking or noise when moving. With arthrosis, there may be a creaking or noise in the joints that occurs with every movement.
- Swelling and redness. In some #1093; In cases of arthrosis, it can lead to swelling and redness of the joint. However, this rarely happens.
- Joint deformity. In the case of a prolonged course of the disease, chronic deformation of the joint may occur, which will also be accompanied by pain and limitation of movement.
If you notice such symptoms, you should consult a doctor who will make a diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
How is arthrosis diagnosed?
Basic diagnostic methods
Different methods are used to diagnose arthrosis. The main ones are:
- Clinical examination of the patient;
- Radiography;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Arthroscopy.
Clinical examination
The clinical examination of the patient is performed by a doctor who examines the joint for pain, swelling, limited mobility and other symptoms of arthrosis. In addition, the doctor asks questions about the nature of the pain, its duration and manifestations in different situations.
Radiography
Radiography allows you to determine the degree of joint damage and identify characteristic changes that are characteristic of arthrosis. This diagnostic method allows you to determine the reduction of joint spaces, the presence of bone sprouts and joint deformities.
M. R. I
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) helps to more accurately determine the nature of joint damage and identify other changes that are not available on radiography.
CT scanner
Computed tomography (CT) is a more accurate method for diagnosing arthrosis than radiography, as it allows you to make a more detailed picture of the joint.
Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy allows you to examine the joint using a special instrument - an arthroscope. This diagnostic method allows you to more accurately determine the degree of joint damage and identify the cause of the development of arthrosis.
Treatment of arthrosis: characteristics depending on the degree of development
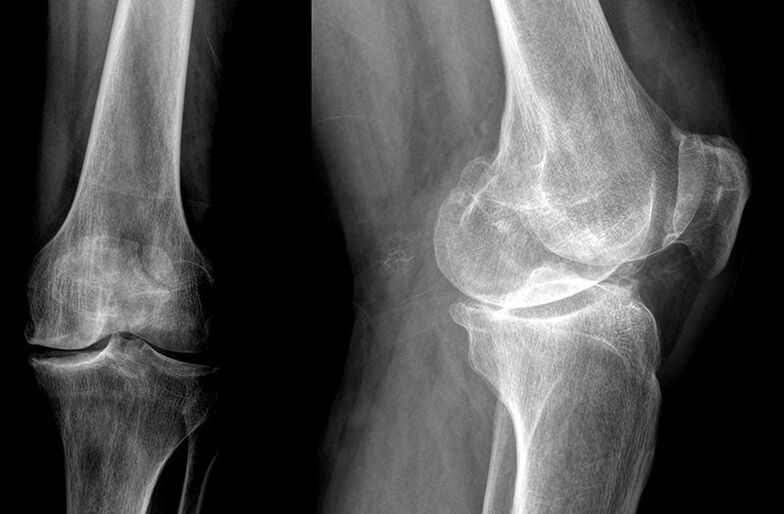
1st degree of arthrosis
In the first stage of the development of arthrosis, it is necessary to take measures to preserve the joints and strengthen the muscular system. Physical activity and moderate exercise will help you strengthen your muscles and prevent further damage to your joints. At the same time, too much stress and a sedentary lifestyle should be avoided.
Arthrosis of the 2nd degree
At this stage of the development of arthrosis, the main task is to reduce pain and prevent further destruction of the joints. In this case, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, as well as the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and healing ointments can help. It is also recommended to do joint and muscle exercises regularly.
Arthrosis of the 3rd degree
In the third stage of arthrosis, there is significant destruction of the joint surface, which can lead to serious movement restrictions. In this case, an operation is often prescribed to restore the joint and restore its functionality. Rehabilitation treatments, including physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises, are also necessary to restore joint function after surgery.
Basic methods of prevention of arthrosis
Maintain a normal body weight
Excess body weight negatively affects the condition of the joints, especially those that are subject to greater stress. In arthrosis, weight is one of the main risk factors for the development of the disease. The greater the weight, the greater the force on the joints and the faster the degenerative process in the cartilage tissue progresses. To prevent the development of arthrosis, it is necessary to control your weight as much as possible and avoid excessive weight gain.
Exercise regularly
Weak muscles, especially weak joint muscles, are risk factors for osteoarthritis. Regular exercises that strengthen body muscles and joints will help prevent the development of arthrosis. It should be remembered that excessive loads on the joints can negatively affect the condition of the cartilage. Therefore, it is necessary to choose exercises that will not lead to significant stress on the joints, but at the same time will help strengthen the muscles.
Choose the right shoes
Shoes, especially those you wear regularly, can have a significant impact on joint health. Avoid wearing high heels, as they can put additional pressure on the knee joints and contribute to the development of arthrosis. You should also avoid very tight and tight shoes, which can lead to incorrect foot placement and increased joint load.
Nutritious food
A nutritious and balanced diet is of great importance for maintaining the health of not only the joints, but also the whole organism as a whole. If you have osteoarthritis, you should increase your consumption of foods rich in calcium and vitamin D, which help strengthen bones and joints. It is also very important to drink enough water to maintain an optimal level of hydration of cartilage tissue.
Follow the rules of hygiene and prevention of joint injuries
Compliance with hygiene rules and prevention of joint injuries will help prevent the development of arthrosis. Do not put unnecessary strain on your joints, do not make sudden movements, do not lift heavy loads and use joint protectors when playing sports.
Complications of arthrosis
Arthrosis is a progressive joint disease that can lead to various complications. One of the most serious complications of arthrosis is the complete destruction of the joint. Once a joint is completely destroyed, little can be done to restore its function and relieve pain.
Other complications of osteoarthritis include limited movement in the joint and loss of functionality. In some cases, surgery may be needed to correct the problem.
Another possible complication of arthrosis is the development of an inflammatory process in the joint. This can lead to pain, swelling and loss of joint function.
Complications of arthrosis can be prevented if you seek help when small changes begin to appear in the joints. In order to reduce the risk of complications, it is important to monitor your health, maintain a healthy lifestyle and regularly consult a doctor for the prevention and treatment of arthrosis.
Osteoarthritis and disability: what you need to know?
What is osteoarthritis?
Arthrosis is a chronic disease of the musculoskeletal system in which joint function is impaired. Recognizable signs are pain in the joints and their deformation. Osteoarthritis can occur in any joint of the body, but the knee, hip and shoulder joints are most commonly affected.
Types and degrees of arthrosis
Depending on which joint is affected, there are several types of arthrosis: knee, hip, shoulder, hand, wrist.
The degree of arthrosis can vary. Mild arthrosis is characterized by mild pain and a limited degree of joint deformation. The average degree of arthrosis is characterized by severe deformation of the joint and painful sensations even at rest. Severe arthrosis is accompanied by impaired joint mobility and severe pain.
Arthrosis and disability
In the case of severe arthrosis, when the mobility of the joints is impaired and the person feels severe pain, you can submit a claim for disability. The decision on the determination of disability is made by the commission after a medical examination. Each case is considered individually, and the decision is made based on the availability of medical indications, which are determined by doctors.
Restrictions for arthrosis and disability
Most people suffering from arthrosis have limitations in their movement, which makes it difficult for them to do their normal activities. When disability is granted, such patients can be provided with additional benefits, for example, benefits, free drugs and medical services, as well as the ability to contact social welfare organizations.
How to maintain healthy joints in arthrosis?
Arthrosis is a chronic disease of the joints that leads to impairment of their functions and degeneration of cartilage tissue. However, there are ways to maintain healthy joints with osteoarthritis.
Maintain a normal weight
Excess weight is the main enemy of the joints. The weight puts additional stress on the joints, accelerating their destruction. Therefore, monitor your weight and, if necessary, reduce it.
Physical activity

Physical activity is essential to strengthen muscles and ligaments, which helps reduce stress on joints. However, strong blows and traumatic loads should be avoided, as they can damage the joints.
Pay attention to nutrition
Diet is an important aspect of joint health. Food rich in calcium and vitamins strengthens bones and joints. However, it is necessary to limit the consumption of fatty, sweet and smoked foods, because they worsen the condition of the joints.
See your doctor
It is important to visit the doctor regularly and monitor the condition of the joints. Osteoarthritis cannot be cured, but the symptoms can be alleviated with treatment and special exercises.
Following these recommendations will help maintain healthy joints with arthritis. It is important to understand that even the slightest discomfort in the joints should be taken seriously and measures should be taken to strengthen them.
Answer to the question:
What is osteoarthritis?
Arthrosis is a chronic joint disease characterized by the destruction of cartilage tissue. As a result, there is deformation and limitation of joint mobility.
What types of arthrosis are there?
There are several types of arthrosis, which differ depending on where the joints are affected. For example, coxarthrosis (arthrosis of the hip joint), gonarthrosis (arthrosis of the knee joint), osteoarthrosis (arthrosis of the fingers and toes), cervical arthrosis (arthrosis of the neck vertebrae), etc.
What are the symptoms characteristic of arthrosis?
Symptoms of arthrosis can vary depending on the severity of the disease. The main symptoms are pain and discomfort in the joints, stiffness and limited mobility, creaking and cracking sounds when moving the joints, swelling and redness of the joints.
What factors can cause the development of arthrosis?
Risk factors that contribute to the development of osteoarthritis may include age, sex, heredity, joint injuries and overloads, obesity, calcium and vitamin D metabolism disorders, and other diseases such as diabetes and gout.
What treatment methods are used for osteoarthritis?
Various methods can be used to treat osteoarthritis, including drug therapy, exercise and rehabilitation measures, massage and physical therapy. In some cases, surgery may be required - endoprosthetics or arthroscopy.
What is the prognosis for people with osteoarthritis?
The life prognosis for people with arthrosis depends on the degree of the disease and the timeliness of treatment. If treatment is not carried out, complications and limitations of joint mobility are possible. By starting treatment on time and following the doctor's recommendations, most patients with arthrosis can maintain a full lifestyle and work.